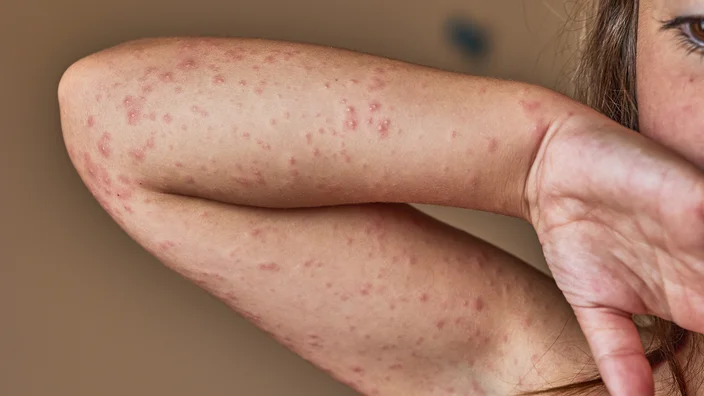
Drug allergies can significantly impact an individual’s health and quality of life. These immune system responses to medications vary from mild reactions, such as rashes or itchy skin, to severe anaphylactic episodes. Early detection and appropriate treatment are necessary to avoid potentially life-threatening complications. Explore common drug allergies, treatment options, and key differences between allergies and side effects.
What Are Common Drug Allergies?
Allergic reactions to medications can range from mild to life-threatening. Understanding the signs of common allergies is beneficial for effective management. Here are three of the most frequently reported drug allergies.
Penicillin
Penicillin is one of the most widely reported allergies. Symptoms can include hives, rash, and swelling, particularly of the face, lips, or throat. Severe reactions may lead to difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis. Treatment options involve immediate drug withdrawal, antihistamines to alleviate mild symptoms like itching or rash, and corticosteroids for extensive inflammation. In cases of anaphylaxis, epinephrine is needed to prevent severe complications. Drug desensitization may be recommended if penicillin is needed for treatment.
Aspirin
Aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can trigger allergic reactions in some individuals. Symptoms may include skin rashes, nasal congestion or swelling, wheezing, shortness of breath, and, in severe cases, anaphylaxis. Treatment involves stopping all aspirin-containing medications immediately. Antihistamines can relieve mild symptoms like nasal congestion or itching, while corticosteroids address more significant inflammation. Epinephrine is necessary for treating anaphylaxis.
Sulfa
Sulfa drugs, often used as antibiotics or diuretics, can cause allergic reactions in certain individuals. Symptoms may include fever, skin rashes or hives, and swelling of the lips, face, or tongue. In rare, severe cases, anaphylaxis can occur. Treatment involves discontinuing the sulfa medication, using antihistamines to alleviate symptoms like itching or hives, and administering corticosteroids for more intensive symptom management. Epinephrine is necessary in severe reactions, and drug desensitization may be used when sulfa drugs are needed for treatment.
How Can You Differentiate Drug Allergies from Side Effects?
While drug allergies involve an immune response, side effects typically result from the pharmacological action of the medication itself. For example, drowsiness from antihistamines or gastrointestinal discomfort from antibiotics are common side effects, not allergic reactions. Differentiating the two is beneficial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
What Are the Treatment Options?
Effective treatments for these specific allergies aim to reduce symptoms and prevent serious complications. Here are the key methods:
- Drug Withdrawal: Stop the medication immediately upon identifying an allergic reaction. This minimizes the immune response and reduces the risk of complications.
- Antihistamines: Relieve symptoms like rashes, itching, and nasal congestion by counteracting the histamine released during an allergic reaction.
- Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and manage more severe allergy symptoms, such as skin reactions, swelling, and respiratory issues.
- Epinephrine: A life-saving treatment for anaphylaxis, an epinephrine injection quickly stabilizes severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or loss of consciousness.
- Drug Desensitization: Used when a specific medication is necessary despite an allergy. Small, controlled doses are administered over time to help the immune system become tolerant to the drug.
Summary and Prevention Tips
Understanding allergies is beneficial for managing symptoms and preventing severe health outcomes. Knowing how to differentiate between common drug allergies and side effects, and exploring effective treatment options, empowers individuals to take an active role in their healthcare. To prevent issues, inform healthcare providers of any known allergies, wear a medical alert bracelet, and avoid self-medicating without consulting a professional. For more advice on drug allergies and treatments, consult a certified allergy specialist to take the first step toward safer medication management.