Physicians utilize a range of tools to assess the structure and function of the heart. Among these diagnostic methods is the echocardiogram, a non-invasive imaging test that provides detailed pictures of the heart. This procedure allows medical professionals to observe the heart as it beats and pumps blood, offering a comprehensive view of its mechanics.
What Is an Echocardiogram?
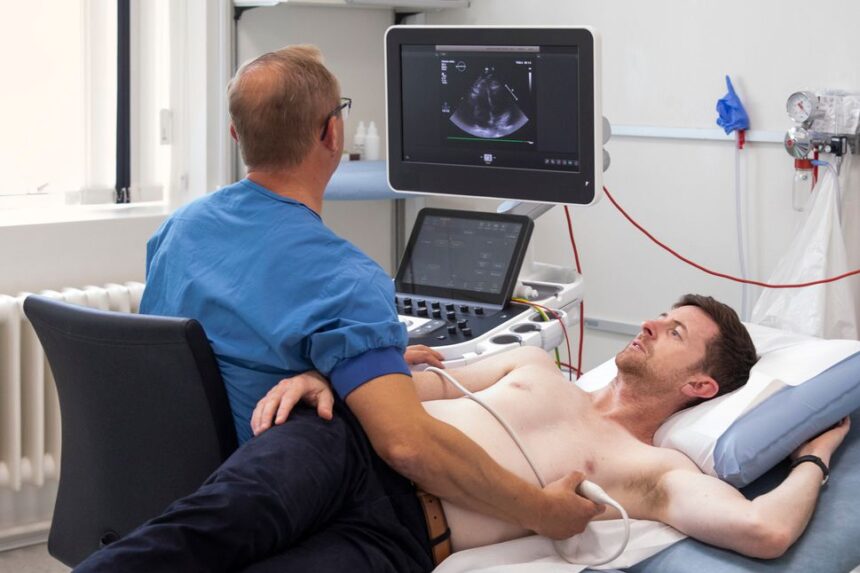
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create moving images of your heart. It is a type of ultrasound that is specifically designed for the heart. The procedure does not involve radiation. A device called a transducer is placed on the chest. This device sends high-frequency sound waves through the chest toward the heart. The sound waves echo off the heart’s structures.
A computer processes these echoes and converts them into real-time images, which are displayed on a monitor. These images display the size and shape of the heart, as well as the function of its chambers and valves. This enables a cardiologist to evaluate the heart’s pumping action and detect any abnormalities in its structure or function.
What Can They Diagnose?
Echocardiograms provide valuable information that can help identify a range of heart conditions. These include abnormalities related to the heart’s structure and function. Among the conditions that may be observed are cardiomyopathies, which refer to diseases of the heart muscle that can impact its ability to pump blood efficiently. Echocardiograms also aid in the assessment of valvular heart disease by providing a detailed view of how the heart valves open and close with each heartbeat.
The imaging can reveal changes in the size and thickness of the heart chambers, features sometimes associated with longstanding high blood pressure or other chronic conditions. Heart failure, which describes a state where the heart is not pumping blood as effectively as it should, may be reflected in the images of the heart’s contraction and relaxation patterns. Other findings that may come to light include masses, such as tumors or blood clots, within the heart.
What Does One Involve?
A standard transthoracic echocardiogram is a straightforward and painless procedure. The sonographer will place small, sticky patches called electrodes on your chest to monitor your heart’s electrical activity with an electrocardiogram (ECG) during the test. They will then apply a special gel to your chest. The sonographer will press the transducer firmly against your skin and move it around to different locations on your chest to get images of your heart from various angles. You may be asked to change positions or hold your breath for short periods to help obtain clearer pictures.
There are no side effects, and you can typically return to your normal activities immediately afterward. Once the images are captured, a cardiologist will review them. The results will then be discussed with you by your physician, who can explain what the findings mean for your heart health.
Meet With a Cardiologist
An echocardiogram is a common and informative diagnostic tool in modern cardiology. If your doctor has suggested an echocardiogram, it is to gain a deeper understanding of your heart. Discussing the results with a cardiologist can provide clarity on your specific health situation and inform any subsequent steps in your care plan.