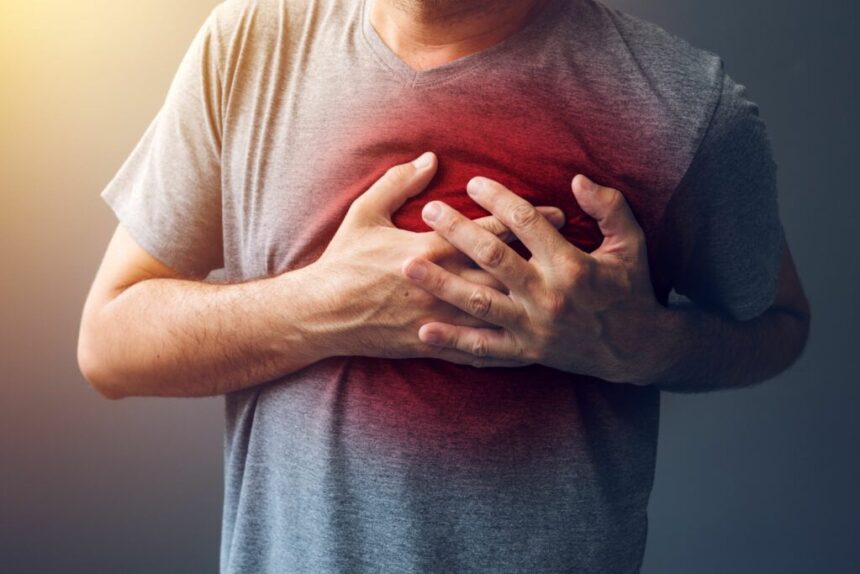
Experiencing chest pain can be unsettling, often bringing a wave of questions and concerns. The discomfort can range from a sharp stab to a dull ache, and its source is not always clear. Understanding the potential causes helps you assess your situation and decide on the appropriate next steps. This guide offers information to help you navigate this common health issue.
What Causes Chest Pain?
Many conditions can cause chest pain, not all of which involve the heart. The discomfort you feel might originate from your lungs, esophagus, muscles, ribs, or nerves. Identifying the source is a task for a medical professional, but knowing the range of possibilities can be helpful.
Here are some common sources:
- Musculoskeletal Issues: Strained chest muscles or bruised ribs from an injury or even from coughing can cause localized pain. This type of pain often worsens with movement or when you press on the affected area.
- Digestive Problems: Acid reflux, or heartburn, is a frequent cause of a burning sensation in the chest. This happens when stomach acid moves up into the esophagus. Gallbladder or pancreas problems can also trigger pain that spreads to the chest.
- Lung-Related Conditions: Conditions such as pneumonia or bronchitis can cause sharp pain that worsens when you breathe deeply or cough. A pulmonary embolism, a blood clot in the lung, is a serious condition that can also cause chest pain.
- Heart-Related Issues: A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing pain that may feel like pressure, squeezing, or fullness. Angina is pain in the chest caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle.
Differentiating between these possibilities on your own can be difficult. The character, location, and duration of the pain provide clues, but a professional diagnosis is the only way to be certain. Your health history and other symptoms play a large part in determining the cause.
When Should You Call 911?
Some symptoms mean you need immediate medical attention. Do not delay seeking emergency help if your chest pain is new, severe, or unexplained. You should call 911 right away if you experience chest discomfort along with any of the following signs:
- Pain that spreads to your arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
- A squeezing, fullness, or pressure in your chest that lasts for more than a few minutes, or goes away and comes back.
- Shortness of breath.
- Breaking out in a cold sweat.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Nausea, especially when it occurs with chest pain.
Acting quickly in these situations can make a significant difference in your outcome.
When Is It Safe to Wait?
Not all instances of chest pain signal an emergency. If the pain is familiar and your doctor has already diagnosed its cause as non-life-threatening, you might not need to call 911. An example is pain you can clearly identify as muscle soreness or diagnosed heartburn.
Pain that is brief, sharp, and improves with a change in position may not be related to your heart. If you can reproduce the pain by pressing on your chest wall, it is more likely to be a musculoskeletal issue. If your doctor has previously given you a plan for managing a known condition that causes chest discomfort, follow those instructions. When you are uncertain, contacting your doctor for guidance is a good first step.
Get Help
Since the cause of chest pain can be challenging to determine, seeking a professional medical opinion is the safest option. A healthcare provider can perform the appropriate tests and ask detailed questions to provide an accurate diagnosis and peace of mind. If you are experiencing chest pain, especially with any concerning symptoms, reach out to a healthcare professional right away.