Cardiac stress tests are diagnostic tools used to assess heart health. They involve monitoring the heart’s performance under physical or pharmacological stress to identify potential issues that may not be apparent when the body is at rest. Healthcare providers rely on these tests to get a clearer picture of how well the heart handles increased demands, making them valuable in evaluating the risk of cardiovascular conditions. Here’s more on cardiac testing:
Benefitting From Cardiac Stress Tests
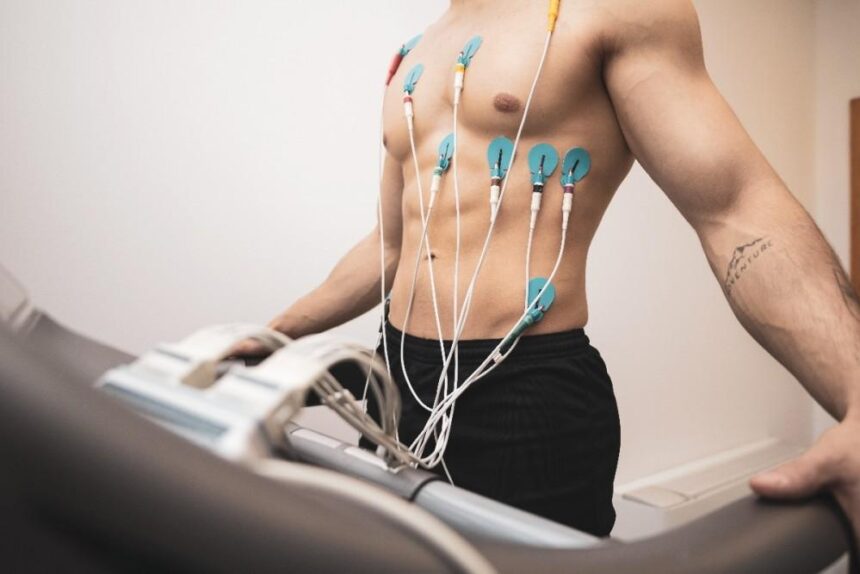
A cardiac stress test measures the heart’s response to stress, usually induced through exercise or certain medications. During the test, a patient is typically asked to walk on a treadmill or pedal a stationary bike. As physical activity increases, medical professionals monitor the heart’s electrical activity, blood pressure, and oxygen levels using equipment like an electrocardiogram (ECG) or imaging tools like echocardiography.
If a patient cannot engage in physical activity, medications are administered to mimic the effects of exercise on the heart. This variation is known as a pharmacological stress test. The goal of a test is to observe how the heart functions when it is working harder. Any irregularities in rhythm, blood flow, or overall function during the test might point to underlying concerns warranting further investigation.
Detecting Heart Conditions
Although a cardiac test cannot definitively diagnose heart conditions, it provides valuable clues about existing or potential problems. These tests are particularly helpful in identifying conditions like:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): A common condition where the arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked by plaque buildup. Tests may reveal symptoms like reduced blood flow, chest pain, or discomfort during activity.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats may become more pronounced under stress. Testing stress can help in identifying abnormal rhythms that may not appear during rest.
- Heart Valve Problems: While not the primary diagnostic tool, tests can sometimes suggest issues with the heart valves that affect blood flow.
- Exercise Tolerance or Limitations: For individuals with known heart conditions, testing can assess how well the heart adapts to increased physical demands and establish safe activity limits.
These insights enable healthcare providers to determine whether additional tests or treatments are necessary.
Impacting Heart Disease Outcomes
Cardiac stress testing works by amplifying the factors that put strain on the heart. When the heart is under stress, conditions, like misaligned blood flow or irregular rhythms, become more apparent. This is why the test is so effective at identifying subtle anomalies that could otherwise go unnoticed during a routine examination.
These tests are typically just one piece in the diagnostic puzzle. Their results may prompt additional, more specialized testing like coronary angiograms or CT scans to confirm findings and guide treatment. Stress testing is used to:
- Monitor Blood Flow
- Detect Electrical Abnormalities
- Provide Imaging of the Heart
Restricted blood flow due to narrowed arteries can cause changes in ECG patterns, abnormalities seen on imaging, or symptoms like chest discomfort during the test. This is often a sign of coronary artery disease. Changes in the heart’s electrical activity under stress may point to arrhythmias. These findings can guide decisions on whether further cardiac monitoring or interventions are needed.
Benefit From a Stress Test Today
Understanding the value of cardiac stress testing in identifying early heart disease indicators can play a key role in maintaining long-term cardiovascular health. If you experience unexplained chest pain, shortness of breath during exercise, or have a family history of heart disease, consulting a healthcare professional about a stress test could provide key insights. By identifying potential issues early, you can explore options for more effective management and prevention strategies. Visit a medical provider today to take proactive steps toward protecting your heart.