Managing joint and musculoskeletal pain has largely revolved around pain relief methods or surgical interventions in the past. Regenerative orthopedics is emerging as a sophisticated avenue that supports the body in healing itself. This field brings a non-surgical, patient-centered approach to orthopedic care, relying on the body’s biological resources to target conditions such as joint degeneration, soft-tissue injuries, and damaged cartilage.
What Is Regenerative Orthopedics?
Regenerative orthopedics is an innovative branch of medicine focused on utilizing the body’s natural healing mechanisms. Rather than managing symptoms or opting for invasive surgical methods, this approach encourages targeted repair or regeneration of tissues. Regenerative orthopedics aims to address damage sustained from injury or conditions such as arthritis. The procedures involved typically use minimally invasive techniques and effective methods for delivering biological materials directly to areas requiring tissue repair.
What Treatments Fall Under It?
Several procedures are categorized under regenerative orthopedics. Two of the more common ones are Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy and Lipoaspirate Therapy. Both leverage the body’s natural abilities and are performed by trained specialists in controlled clinical environments.
PRP Therapy
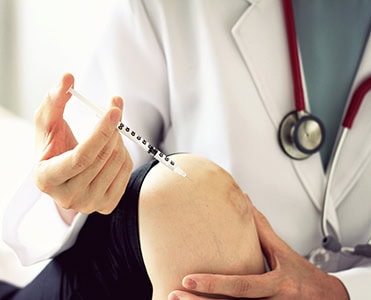
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy involves extracting a patient’s blood, concentrating its platelets and growth factors, and reinjecting this enriched plasma into the targeted area. Platelets within the blood contain several growth factors known to support healing, promote tissue repair, and reduce inflammation. PRP therapy has been explored for conditions such as osteoarthritis. Its appeal lies in its ability to provide targeted support with a substance derived directly from the patient, minimizing risks commonly associated with external materials or medications.
Lipoaspirate Therapy
Lipoaspirate Therapy utilizes adipose (fat) tissue cells collected from the patient. This fat contains cells that may assist in supporting injured or damaged tissue. During this procedure, a small amount of fat is extracted, processed to concentrate the necessary cells, and injected back into the affected area. Like PRP therapy, its minimally invasive nature is an appealing feature for those searching for options outside surgery.
What Does Treatment Look Like?
Patients exploring regenerative orthopedics should expect a professional evaluation to determine whether these therapies align with their specific needs. While the details vary based on the treatment chosen and the condition being addressed, there are several general steps involved.
- Evaluation: Medical practitioners will first perform an assessment, which may include imaging tests and a full discussion of the patient’s medical history alongside their symptoms.
- Preparation: For therapies like PRP and lipoaspirate, a small amount of the patient’s blood or adipose tissue is drawn carefully using minimally invasive procedures.
- Processing: Once collected, the blood or tissue undergoes processing to concentrate the beneficial substances. During PRP therapy, a centrifuge is often used to separate components of the blood.
- Injection: The processed sample is reinjected into the targeted area under careful guidance, often using advanced imaging to facilitate precision placement.
- Recovery and Monitoring: Most procedures are outpatient, allowing patients to resume everyday activities after treatment. Practitioners may recommend avoiding strenuous activity during initial recovery and might request follow-ups to monitor progress over time.
Approach an Orthopedic Specialist About Treatment
Regenerative orthopedics represents an advancement in medicine, offering approaches that align with the body’s natural mechanisms for healing. Whether managing joint pain, tendon injuries, or other musculoskeletal conditions, these therapies provide alternative avenues to traditional surgical paths. If regenerative orthopedics sounds like something that could align with your needs, reaching out to a trained orthopedic specialist can provide further details.