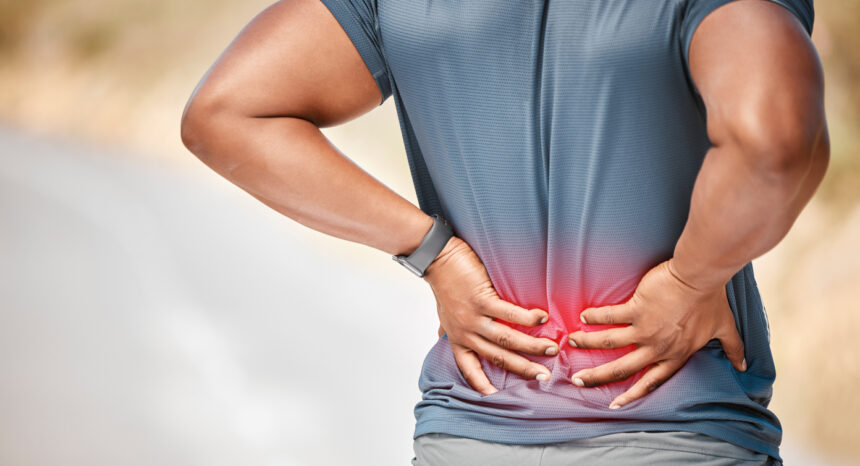
Millions of people struggle with persistent back pain that affects their daily activities and quality of life. Understanding what causes chronic back pain can help you recognize when to seek professional help and what treatment options might work best for your situation. Several factors contribute to ongoing back pain, including muscle problems and structural issues in the spine.
Could Muscle Strain Be Responsible?
Muscle strain remains one of the most common reasons people experience chronic back pain. When you lift heavy objects incorrectly, maintain poor posture for extended periods, or suddenly twist your back, you can overstretch or tear muscle fibers. These injuries often heal within a few weeks, but repeated strain can lead to ongoing discomfort.
Your back muscles work constantly to support your spine and maintain proper posture. If certain muscles become weak or imbalanced, other muscles must work harder to compensate. This extra workload can create tension and pain that persists for months. Poor sleeping positions, stress, and lack of regular exercise also contribute to muscle-related back pain.
How Do Spinal Issues Contribute?
Your spine is a complex structure that plays a key role in supporting your body and allowing movement. Over time or due to injury, issues arise that cause pain and discomfort. Here’s what you need to know about common spinal problems:
- Damaged discs: The cushioning discs between your 33 vertebrae act as shock absorbers. When these discs are damaged, they can bulge or herniate, pressing on nearby nerves and causing symptoms like leg pain or numbness in the extremities.
- Degenerative changes: With age, spinal discs lose moisture and height, while vertebrae can develop bone spurs. These changes may lead to spinal stenosis, a condition where spaces for nerves become narrow, causing pressure and discomfort.
- Spinal arthritis: Arthritis in the small joints of your spine may lead to chronic inflammation and pain. Without proper management, this condition can significantly affect your quality of life.
Understanding these potential spinal issues is the first step toward preventing or effectively treating them. If you experience persistent pain or mobility issues, seeking medical advice may help address the problem and improve your overall spinal health.
Do Joint Problems Cause Pain?
The facet joints in your spine allow for movement while providing stability between vertebrae. When these joints become inflamed or worn down, they can generate significant back pain. Arthritis commonly affects these joints, causing stiffness and discomfort that worsens with activity.
Sacroiliac joints connect your spine to your pelvis and can become a source of chronic pain. These joints may become inflamed due to pregnancy, arthritis, or injury. The pain often feels like it originates in your lower back but may radiate to your buttocks or thighs. Joint problems frequently develop gradually, making them difficult to identify without professional evaluation.
Inflammation in any of your spinal joints can trigger a cycle of pain and muscle tension. When joints hurt, surrounding muscles often tighten to protect the area. This protective response creates additional stress on other parts of your back, leading to widespread discomfort.
Visit a Back Pain Specialist
Chronic back pain rarely improves without proper treatment and lifestyle changes. A healthcare provider can evaluate your condition, identify the cause of your pain, and recommend options like imaging studies, physical therapy, or other treatments. Schedule an appointment with a specialist who can create a personalized treatment plan. Early intervention is key to better outcomes and preventing your condition from worsening.