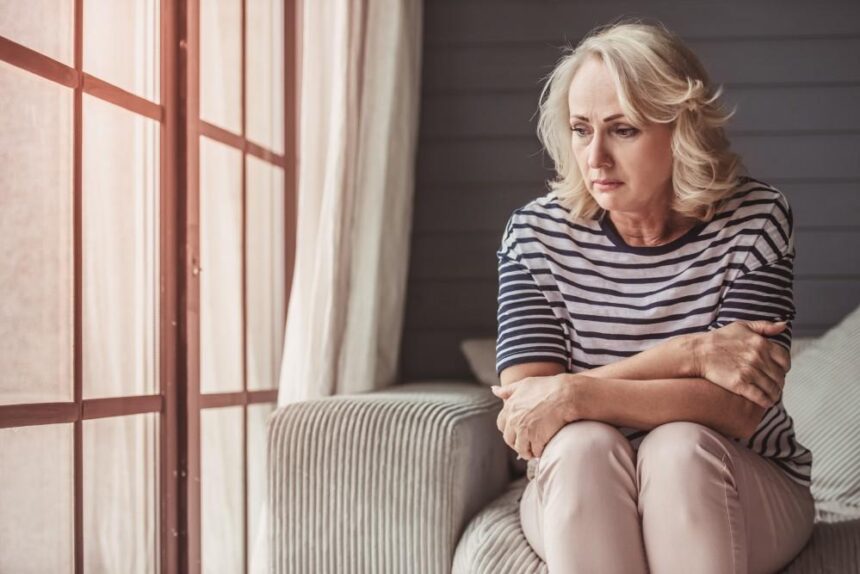
Menopause is a biological transition marked by a wide range of symptoms that can affect daily life and overall well-being. These symptoms vary greatly but often include hot flashes, night sweats, changes in menstrual cycle, sleep disturbances, mood swings, difficulty concentrating, and joint pain. Many women also experience physical changes like vaginal dryness, skin or hair changes, and shifts in body weight. Here’s more information on menopause and how it impacts different aspects of health:
Understanding Perimenopause
The journey to menopause begins with perimenopause. This is the transitional phase leading up to menopause, typically starting in a woman’s 40s, although it can begin earlier or later. Perimenopause marks the time when hormone levels, particularly estrogen and progesterone, begin to fluctuate. These fluctuations may cause irregular menstrual cycles, heavier or lighter periods, and a range of symptoms that may impact daily life.
During this phase, it’s key to monitor health changes, as they may provide early indications of how the body will respond when menopause is reached. While this transitional stage is temporary and often lasts several years, its effects on physical, emotional, and mental health can vary significantly from one woman to another. Some common symptoms of perimenopause include:
- Sleep Disturbances
- Changes in Libido
- Hot Flashes
- Mood Swings
Reaching Menopause
Menopause is officially diagnosed when a woman has gone a full year without a menstrual period. For most women, this occurs between their late 40s and early 50s. This biological stage signals the end of reproductive years, as the ovaries stop releasing eggs and estrogen production declines substantially.
This phase is a natural biological process, but it is often accompanied by notable physical and emotional changes. Vaginal dryness and decreased bone density are common concerns that can develop during this stage of life. Many of these changes are due to the hormonal shifts that occur as the body adjusts to lower levels of estrogen and progesterone.
Impacting Overall Health
Menopause not only brings about changes in reproductive health but also has broader implications for overall well-being. Its impact varies, but it can influence multiple aspects of physical and emotional health. The decrease in estrogen may lead to drier skin and thinning hair. Collagen production also slows, which may contribute to visible signs of aging, like wrinkles and reduced skin elasticity. Here are some other key areas affected by menopause:
Cardiovascular Health
Lower estrogen levels during this biological stage may contribute to a higher risk of heart-related conditions. Estrogen helps your body utilize calcium and regulate cholesterol, so its decline can lead to an increased risk of high blood pressure and heart issues. This is why maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle becomes even more impactful during this time.
Bone Density
Estrogen plays a fundamental role in maintaining bone density. When levels drop, bones may weaken, increasing the risk of osteoporosis. Many women experience a decline in bone strength during and after menopause, making them more susceptible to fractures.
Weight Changes
Hormonal changes can make it more challenging to maintain a stable weight. Many women report weight gain during menopause, particularly around the abdomen. This may also impact metabolic health, increasing the risk of developing conditions like diabetes.
Cognitive Function
Some women notice memory lapses or difficulty concentrating during menopause, often referred to as “brain fog.” Anxiety, irritability, and mood swings are commonly reported symptoms. Sleep disturbances, often caused by night sweats, may further exacerbate feelings of fatigue and stress.
Learn More About Menopause
Menopause is a natural transition that affects every woman differently. While it can bring challenges, understanding its impact and adopting proactive steps to maintain overall health can ease the process. Maintaining an active lifestyle, following a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, prioritizing adequate sleep, and seeking medical advice when needed can all contribute to effectively managing the effects of menopause. Visit with a provider today to learn more and receive personalized care.