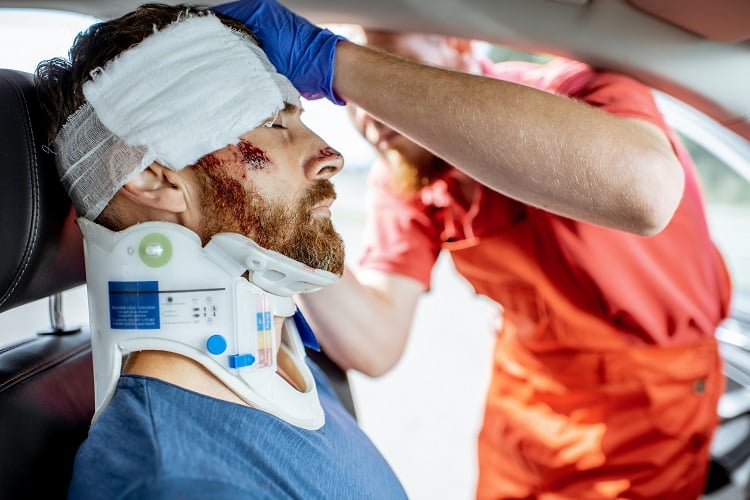
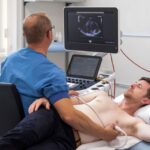
Car accidents can lead to a broad range of physical injuries, from whiplash to broken bones. The injuries vary in type and severity, guided by factors such as collision speed, point of impact, and safety restraints. Recognizing typical car accident injury patterns and knowing general treatment approaches is a key aspect of managing recovery after a collision. Here are some common injuries that result from car collisions and how they’re addressed:
Soft Tissue Injuries
Motor vehicle collisions can cause a variety of soft tissue injuries, affecting the muscles, ligaments, or tendons. These injuries present in different ways depending on the area impacted. Whiplash is a common result, usually involving the neck when the head is rapidly forced backward and forward. This motion strains muscles and ligaments; it leads to symptoms such as pain, stiffness, headaches, and reduced range of motion. Management includes rest, guided movement exercises, and pain control strategies.
Other soft tissue injuries include bruises and strains or sprains of the back, shoulders, or knees. Bruises result from damaged blood vessels beneath the skin, sprains involve stretched or torn ligaments, and strains affect muscles or tendons. Standard approaches for these injuries may involve rest and ice application to reduce swelling. Compression and elevation of the affected area also support healing in some cases.
Head and Brain Injuries
Head injuries can follow high-force impacts, such as when occupants strike a steering wheel, dashboard, or window during an accident. Awareness of this type of car accident injury is fundamental for timely intervention. A concussion is a type of mild traumatic brain injury, and it occurs when a blow to the head moves the brain within the skull. Symptoms may emerge gradually, including headache, confusion, dizziness, memory difficulties, or changes in mood.
Healthcare providers generally recommend physical and cognitive rest as a helpful means of supporting brain recovery. More severe traumatic brain injuries, such as those involving internal bleeding or tissue damage, require prompt and specialized evaluation. Their treatment may include imaging studies, such as CT or MRI scans, surgery to relieve pressure or repair damage, and close monitoring of neurological function.
Chest and Abdominal Injuries
Chest and abdominal injuries can result from impact with components inside the vehicle or the force of a seat belt. These injuries range from chest wall bruising and fractured ribs to deeper injuries involving internal organs, such as the lungs or heart. Key signs like pain or trouble breathing require prompt medical assessment.
The seatbelt, despite its life-saving role, may cause bruises or compressive injuries to organs in the abdomen. When symptoms include persistent pain, tenderness, or swelling in the abdominal area, consultation with healthcare professionals becomes fundamental to rule out internal damage. These types of injuries are treated with pain management, monitoring for internal bleeding or organ damage, and surgical intervention to repair affected tissues or organs when necessary.
Musculoskeletal Injuries
Car accidents subject the body to sudden, forceful impact; this can lead to broken bones or dislocations. Treatment for fractures generally involves immobilization with a cast, splint, or brace to stabilize the bone and support healing. In severe or complex cases, surgical intervention with specialized hardware may be required to promote proper alignment.
Dislocations occur when bones are forcibly displaced from their joints, commonly affecting the shoulders or hips. Management may involve manual repositioning of the joint by a trained healthcare provider. This is followed by a period of immobilization and guided rehabilitation to restore function and strength.
Get Help for Your Car Accident Injury
Identifying common injury patterns from car accidents, such as soft tissue damage, head trauma, chest injuries, and bone fractures, helps promote timely medical evaluation. Individuals in a recent collision should monitor symptoms, track changes, and contact healthcare providers for evaluation. Prompt attention to injuries, combined with awareness of these common conditions, helps support recovery and long-term health. Visit an urgent care facility for additional evaluation.