Bunions are a common foot condition that can significantly impact daily activities and overall foot health. Explore the connection between bunions and foot joint pain, along with treatment options and tips for maintaining healthy feet. Learn about how bunions develop, the discomfort they cause, and their impact on foot health and mobility.
What is a Bunion and How Does it Form?
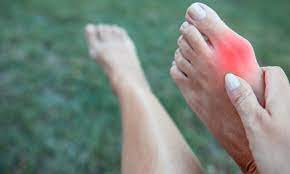
A bunion is a bony protrusion that develops at the base of the big toe or, less commonly, at the base of the little toe (often referred to as a bunionette). This deformity occurs when the big toe shifts inward toward the other toes, pushing the joint outward.
The resulting bump typically worsens over time if left untreated. Several factors contribute to the formation of bunions, including genetic predisposition, foot structure, and external factors like shoes that are too tight or narrow. Some cases also arise from conditions such as arthritis, which can weaken or inflame the joints.
What Are the Symptoms and Pain Points of Bunions?
Bunions can present a range of symptoms that vary in severity. These symptoms often include:
- A visible bulge at the base of the big toe joint.
- Pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area.
- Limited movement of the big toe joint.
- Calluses or corns due to overlapping toes.
- Difficulty finding comfortable footwear.
For some individuals, bunions can cause persistent discomfort, while others experience intermittent pain. Regardless, the condition can lead to other foot-related complications if left unaddressed.
What Is the Connection Between Bunions and Foot Joint Pain?
Bunions and foot joint pain are closely linked. When a bunion alters the alignment of the foot, it can place excess pressure on adjacent joints, leading to discomfort or inflammation. Misalignment can interfere with the natural mechanics of walking, causing stress on nearby areas such as the midfoot, the ball of the foot, or even the ankle.
Complications such as bursitis, hammertoe, and metatarsalgia often occur in conjunction with bunions. These secondary issues can exacerbate joint pain and further restrict mobility.
How Can You Take Preventative Measures and Care for Your Feet?
Preventing bunions or managing minor cases involves adopting healthy foot care practices, such as:
- Wearing well-fitted, supportive footwear with ample toe space.
- Avoiding high heels or shoes with pointed toes for extended periods.
- Strengthening foot muscles through targeted exercises.
- Monitoring for early signs of bunions and addressing them promptly.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the feet.
These strategies can help minimize the risk of bunion formation or progression while promoting overall foot health.
When Should You Consult a Podiatrist?
Individuals experiencing persistent foot pain, a worsening bunion, or difficulty walking should consult a podiatrist for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment. During the consultation, the podiatrist will:
- Assess the severity and alignment of the bunion.
- Discuss treatment options, including both conservative and surgical approaches.
- Provide guidance tailored to the individual’s condition and lifestyle needs.
Consult a Podiatrist Today
Bunions can cause significant discomfort and contribute to broader foot health issues. By understanding their formation, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring both treatment and prevention methods, individuals can take control of their foot health.
For those seeking professional guidance, consulting a podiatrist can aid in an effective and personalized treatment plan. To learn more about bunion care and treatment options, schedule an appointment with a podiatrist today.
Related Articles
When To Seek Professional Help for Persistent Back Pain
Understanding the Role of an Internist in Chronic Disease Management
How Sports Doctors Helps with Rehabilitation Before and After Surgery